Many people wonder: what’s the quickest way to bring down high blood sugar levels through physical activity? It’s no surprise that healthcare professionals often emphasize the importance of exercise in maintaining overall health. Regular physical activity not only helps with weight management but also reduces the risk of chronic conditions such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes. For those already living with diabetes, the stakes are even higher—keeping blood sugar levels in check can prevent potentially severe complications.
When considering what type of exercise is most effective, think less about intense gym routines and more about simple, consistent activities that fit into daily life. Let’s explore how exercise influences blood sugar levels and identify the activities that can help lower them most efficiently.

How Does Exercise Impact Blood Sugar?
Exercise helps the body become more sensitive to insulin, the hormone responsible for moving glucose from the bloodstream into cells. As soon as you start moving, your muscles begin using glucose for energy, often leading to an immediate drop in blood sugar [1]. Over time, consistent physical activity improves glucose metabolism and overall insulin efficiency, creating long-term benefits for blood sugar control.
Short-Term Effects:
When you engage in exercise, you might experience a temporary spike in blood sugar due to the release of adrenaline. However, this is quickly followed by a significant decrease as your muscles draw in glucose for energy. This effect is especially noticeable after high-intensity exercises, where your body continues to burn glucose even after you’ve stopped working out [2].
Long-Term Effects:
Regular physical activity enhances your cells’ responsiveness to insulin and helps maintain a stable glucose level. Over time, this can improve your HbA1c levels, a key measure of long-term blood sugar control [3]. Consistent exercise also aids in weight management, reduces insulin resistance, and can even lower the need for certain diabetes medications.
The Best Exercises for Lowering Blood Sugar
Aerobic Exercises
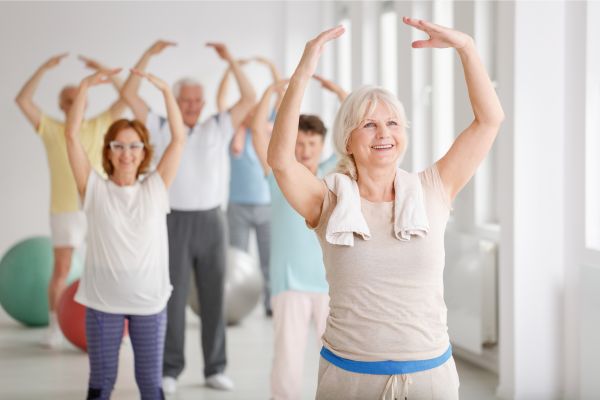

Activities like walking, jogging, cycling, swimming, and dancing are highly effective at reducing blood sugar levels. These exercises elevate your heart rate, increase your breathing rate, and encourage your muscles to use glucose efficiently. For the best results, choose an activity you enjoy and can do regularly—consistency is key [4].
Tai Chi
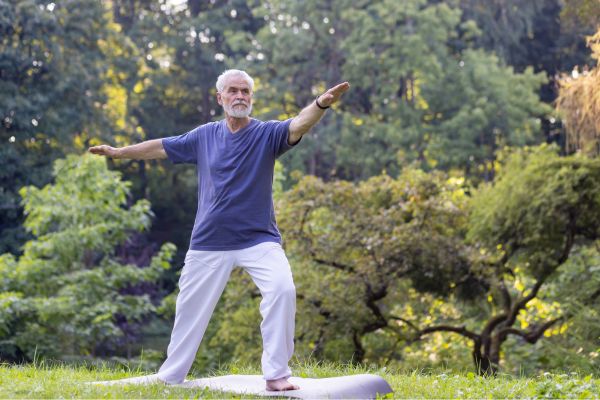

Tai chi is a gentle, low-impact martial art known for its stress-reducing benefits. While it might not seem like an obvious choice, studies show that tai chi can improve insulin sensitivity, promote glucose uptake by muscles, and even help with weight management. Its calming effects also help lower cortisol, a stress hormone that can negatively impact blood sugar levels [5].
Strength Training (Anaerobic Exercise)
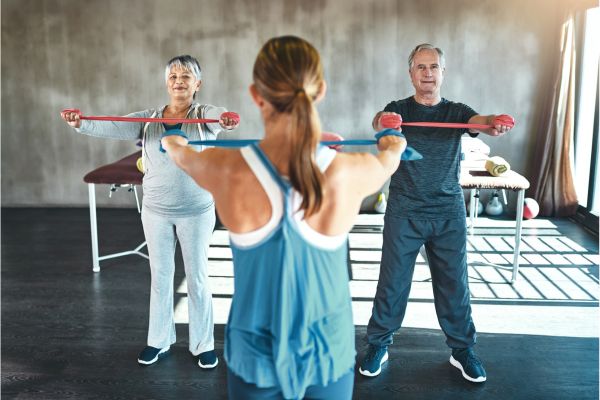

Lifting weights, using resistance bands, or performing bodyweight exercises can help stabilize blood sugar by building muscle mass. Muscles store glucose as glycogen, so increasing muscle size provides more storage space for glucose, keeping it out of the bloodstream. Over time, this can result in better glucose regulation and a lower risk of blood sugar spikes.
Staying Safe While Exercising
If you have diabetes or experience frequent blood sugar fluctuations, it’s essential to exercise safely. Consult your healthcare provider before starting a new routine and monitor your blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise. If your blood sugar is low, consider the “15-15 rule”: consume 15 grams of carbohydrates, wait 15 minutes, then recheck your levels. Repeat if necessary. Remember, the goal is to stay safe and maintain steady glucose levels while reaping the benefits of regular physical activity.
Building a Sustainable Exercise Habit
Finding the motivation to exercise regularly can be challenging, but it’s crucial for long-term blood sugar management. Some strategies include:
- Establishing a Routine: Set aside a specific time each day or week for exercise.
- Working Out With a Partner: Exercising with a friend or joining a group can provide accountability and make the activity more enjoyable.
- Tracking Progress: Use a fitness tracker or journal to monitor improvements, which can motivate you to stay consistent.
Final thoughts
Exercise is a powerful tool for managing blood sugar. Aerobic activities, tai chi, and strength training all offer unique benefits for lowering glucose levels. By incorporating these exercises into your routine, staying mindful of your body’s signals, and seeking guidance from healthcare professionals, you can take control of your blood sugar and improve your overall well-being.
References
- Rd, A. S. M. (2024). 14 easy ways to lower blood sugar levels naturally. Healthline.
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/14-ways-to-lower-blood-sugar - Why does exercise sometimes raise blood glucose | ADA. (n.d.). Retrieved from
https://diabetes.org/health-wellness/fitness/why-does-exercise-sometimes-raise-blood-sugar - Wang, M., & Hng, T. (2021). HbA1c: More than just a number. AJGP, 50(9), 628–632.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34462769/ - Trefts, E., Williams, A. S., & Wasserman, D. H. (2015). Exercise and the regulation of hepatic metabolism. In Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science (pp. 203–225).
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4826571/ - Sauer, M. (2018, December 1). 11 Ways Tai chi can benefit your health. Healthline.
https://www.healthline.com/health/tai-chi-benefits